Case Study: Evaluation of several process cell lysis reagents as replacements for Triton X-100 for rAAV production.
E Neveu, A Parcelier, N Avenier, D Desravines, C Rousseaux, B Mullan, and S Charrier.
Triton X-100 is a detergent used to lyse production cells and release AAVs during rAAV manufacturing processes, which also has a complementary activity of detergent viral inactivation on enveloped adventitious viral contaminants. Due to its degradation to 4-tert-octylphenols, which have harmful endocrine effects, the use of Triton X-100 is no longer permitted by the European Union (REACH regulations).
In this work, we have evaluated four different cell lysis reagents for rAAV production and also for viral detergent inactivation properties. For cell lysis, results show that the required duration of cell lysis (10, 30, 60, 90 and 150 min) is different for each lysis reagent, but after 150min of incubation, a comparable rAAV production is reached for all agents. Secondly, the lysis reagents do not have similar efficiency as regards adventitious viral inactivation compared to Triton X-100. As previously shown by others, we have confirmed that Polysorbate-type reagents are sufficient to lyse cells, but not to inactivate enveloped viral particles and it is necessary to add a solvent such as TnBP, which is already used for viral inactivation in plasma products, to ensure viral inactivation.
Regarding our results, a new detergent, Simulsol (SL-11W) seems to be promising for both cell lysis and adventitious viral inactivation, and has the advantage that an additional solvent is not required to be added for adventitious viral inactivation effects. Whereas Triton X-100 and SL-11W have distinct membrane-disruptive effects in terms of their mechanisms of action, we have confirmed SL11-W effects cells lysis during the production of rAAV2/8 and rAAV2/9 vectors (bulk harvest) and have also demonstrated its efficacy for viral inactivation.
In conclusion, different polysorbate detergents demonstrate different properties (required incubation times) for AAV process cell lysis and require additional solvents if adventitious viral agent inactivation is also desired, and SL-11W is a potential candidate to replace Triton X-100 for rAAV production.
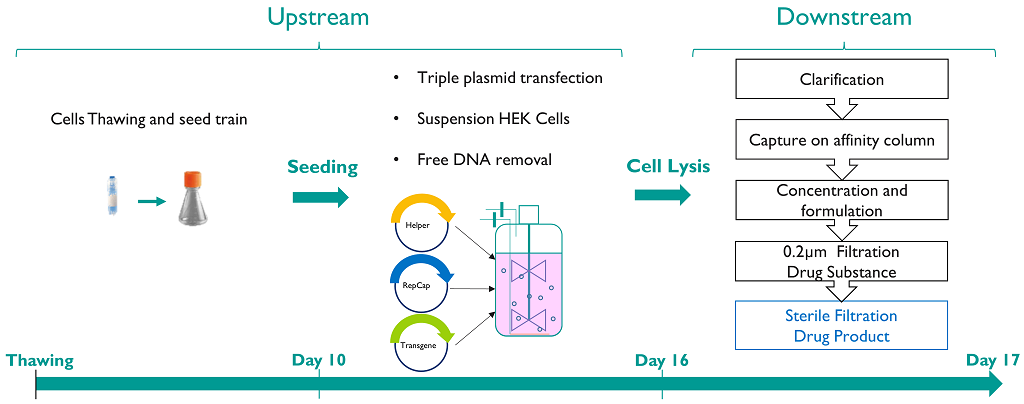
rAAV Process
The production of rAAV vectors requires:
- The recombinant vector genome composed of the gene of interest (GOI) and the regulatory elements for the transgene expression in target cells (promoter, poly A, introns…) flanked by inverted terminal repeats (ITRs);
- The AAV rep and cap genes provided in trans;
- Adenovirus helper functions for efficient replication and rescue of the recombinant genome.
rAAV vectors are produced by triple plasmid transient transfection in HEK293 cells. Before the cell culture clarification and the purification of the vectors to obtain the final drug substance (DS), process cell lysis is necessary to enhance the yield of rAAV particles. Triton X-100 has been historically used to lyse production cells and release AAVs, but also for its complementary activity of viral inactivation on enveloped adventitious viral contaminants. However, because Triton X-100 is no longer authorised for use in the EU due to its harmful endocrine effects, new lysis reagents will be required for AAV manufacturing processes.
Lysis reagent efficiency on HEK293 cells
We have evaluated several reagents in parallel for their impact on the lysis of HEK293 cells during the production of rAAVs. Four reagents have been tested: Polysorbate 80 (PS80), Simulsol (SL-11W) and two commercial Lysis buffers (A and B). These reagents were added to the culture medium and after different incubation times (10, 30, 60, 90 and 150 minutes), cells were harvested to measure the quantity of viable cells after treatment with a NC200 NucleoCounter device (Chemometec). Several concentrations of SL-11W have also been compared to determine the best conditions to use.
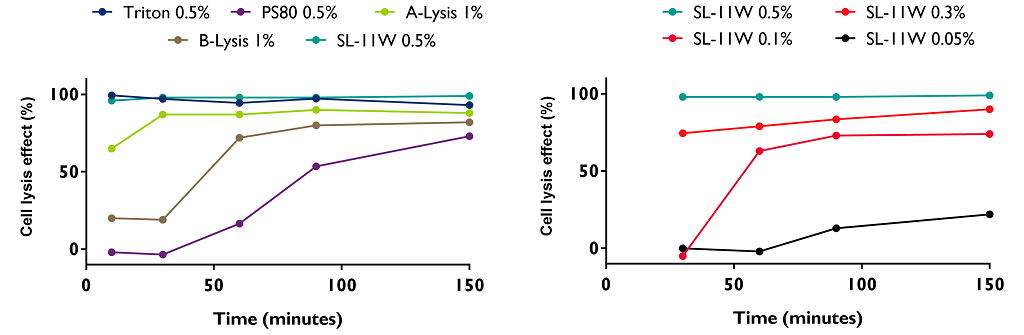
- The time incubation of cell lysis time is dependent on the reagent used;
- At 150 minutes, all the reagents had a cell lysis effect;
- SL-11W needs to be used at 0.5% to reach a cell lysis effect higher than 90% after 30 minutes incubation.
Lysis reagent evaluation on viral inactivation
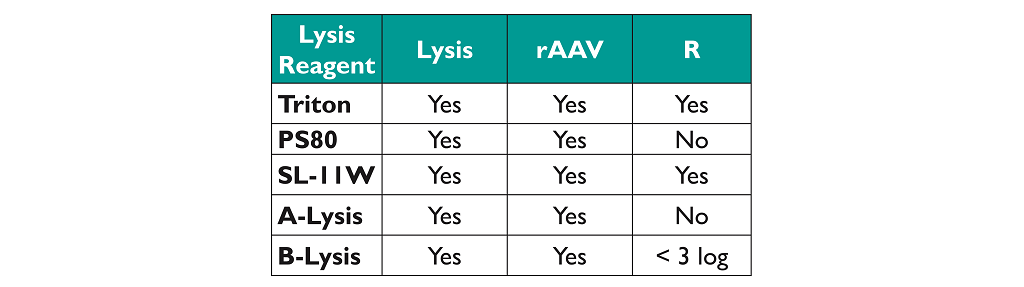
Because Triton X-100 is a detergent which has adventitious viral inactivation properties, we tested the effect of the four reagents on the infectivity of enveloped viruses before and after lysis treatment. We developed an assay based on the transduction ability of enveloped lentiviral vectors, treated or untreated with lysis reagents. The infectious titres obtained before and after lysis agent treatment enabled the calculation of a reduction factor (R).
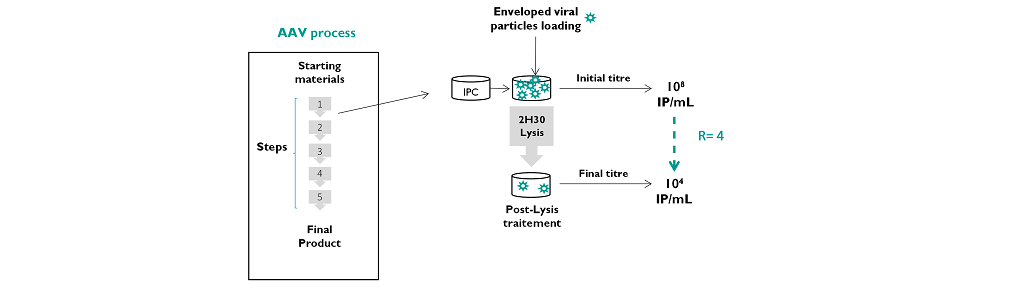
The formula is detailed as following : R = log_10〖((𝐼𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑟𝑒)/(𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑇𝑖𝑡”re” ))〗
*Where the final titre is not determined, it is replaced by the titre defined at the detection limit of the assay.
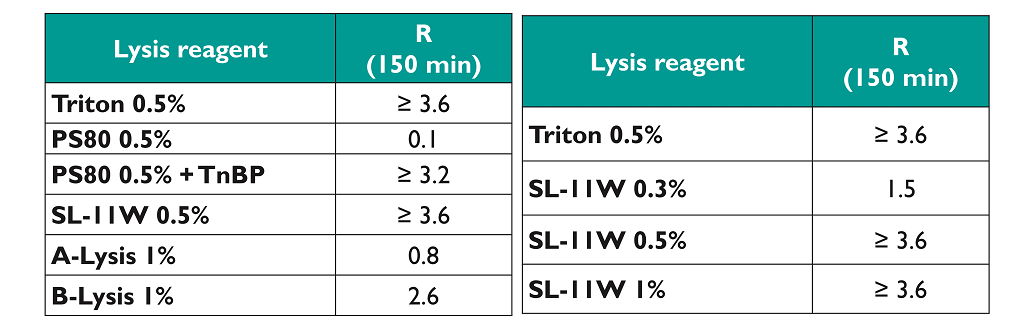
- Only SL-11W has an impact of the inactivation of enveloped viral particles equivalent to Triton X-100;
- Lysis Buffer B has an impact on the inactivation of enveloped viral particles with a reduction factor lower than 3 log;
- PS80 needs the addition of a solvent (TnBP) to effect viral inactivation;
- SL-11W needs to be used at a concentration of 0.5% to reach an inactivation of enveloped viral particles equivalent to the Triton X-100;
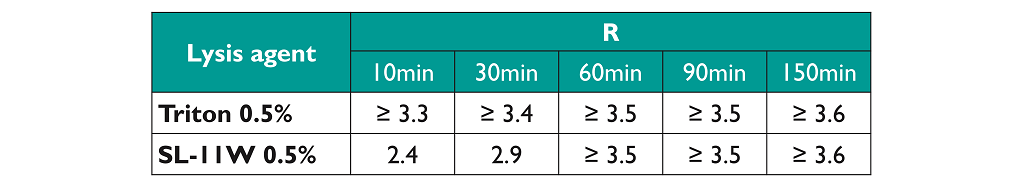
- SL-11W at 0.5% requires a minimal duration of 60 minutes to effect inactivation of enveloped viral particles equivalent to Triton X-100.
Lysis reagent evaluation on rAAV productivity
rAAV vectors were produced at small-scale (shake flasks). The cell lysis step was performed separately for each of the four lysis reagents, applying 2h30 of incubation before harvesting. Titres in crude lysates were determined by qPCR for viral genome and by ELISA for the capsid detection.
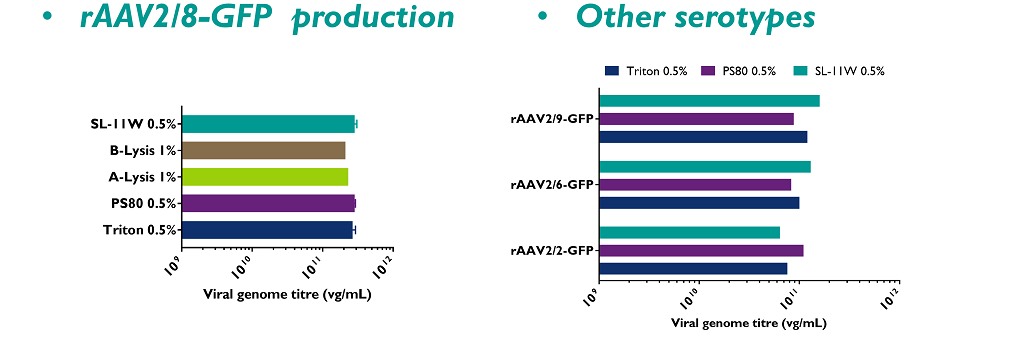
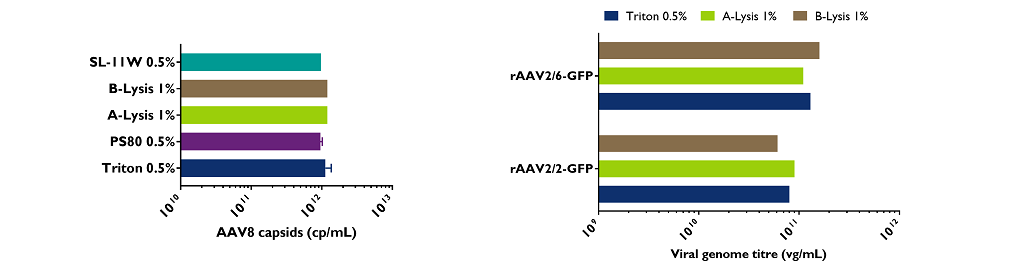
- AAV capsids are not affected by detergents and titres of rAAV2/8-GFP are similar regardless of cell lysis reagent;
- The four cell lysis reagents are efficient for production of rAAVs, regardless of serotypes.

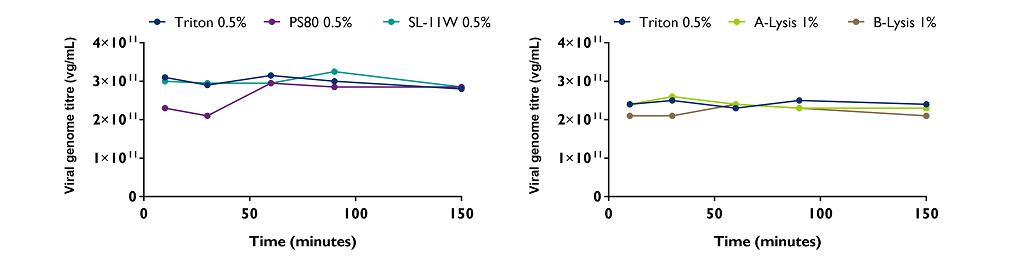
For rAAV2/8-GFP production, the four lysis reagents were individually incubated for 10, 30, 60, 90 and 150 minutes. Crude lysates were harvested at the end of each incubation time.
- As previously seen for cell lysis efficiency and viral inactivation, the duration of incubation with the lysis reagent is important to release the maximum quantity of rAAV vector.
Conclusion
In this work, several reagents have been evaluated for their cell lysis and viral inactivation properties and their conditions of use for rAAV production (duration and concentration), in comparison to Triton X-100.
- Polysorbate 80 requires an additional agent (TnBP) to reach equivalent activities of viral inactivation as Triton X-100. It will be important to evaluate if this combination could be used for rAAV production at manufacturing scale, as already used for plasma products.
- Simulsol (SL-11W) could be a potential candidate to replace Triton X-100, due to its similar activities (lysis detergent and viral inactivation) without impact on rAAV production.


